This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon associate, Google associate as well as associate for other programs, Guitar & Music Institute may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.

Embarking on the journey to improve sight reading skills? You’re not alone! Enhancing your ability to sight read serves as a fundamental tool for musicians across the globe and across all genres. Whether you’re an aspiring virtuoso or a hobbyist looking to indulge in the joy of instant music-making, the right sight reading practice can make all the difference. From classical to jazz, your proficiency in reading music effortlessly propels you to higher levels of artistry.
Well-structured music sight reading tips can be transformative, teaching you not just to read, but to translate what you see into what you play — and to do it on the fly. Not sure how to get better at sight reading? Fret not! It’s all about learning the techniques, drilling the fundamentals, and practicing effectively. Ready to dive in?
Key Takeaways
- Integrate visual and instrumental skills through targeted exercises to enhance sight reading.
- Develop a fundamental understanding of key signatures, rhythms, and bowing patterns for a solid base.
- Utilize metronomes and practice tools to maintain rhythm and improve accuracy.
- Set incremental goals to make sight reading practice a consistent part of your musical development.
- Learn to anticipate musical notation with quick, effective eye movements for improved execution.
Understanding the Basics of Sight Reading
If you wish to elevate your musical talents, comprehending the foundational elements of sight reading is pivotal. Sight reading exercises not only bolster your ability to perform new pieces with confidence but form the bedrock for your musical literacy. Let’s delve into the core aspects that will set the stage for your journey in mastering music sight reading.
Grasping Music Notation
Imagine being able to glance at a sheet of music and instantly converting those dots and lines into melodious sound. That’s the goal of music sight reading and it starts with music notation. Notation serves as the map of music; it guides you through the terrain of melodies and harmonies. Dedicating time to understand each symbol and its purpose bridges the gap between the notes on the page and the music in your heart.
Recognizing Key and Time Signatures
Any seasoned musician will tell you that recognizing key and time signatures is essential in knowing what you need to do to sight read better. Key signatures determine the scale of the music, thus affecting the pitch of notes, while time signatures lay down the rhythm’s framework. Accurate identification of these elements ensures you’re interpreting the music as intended, right from the onset of your performance.
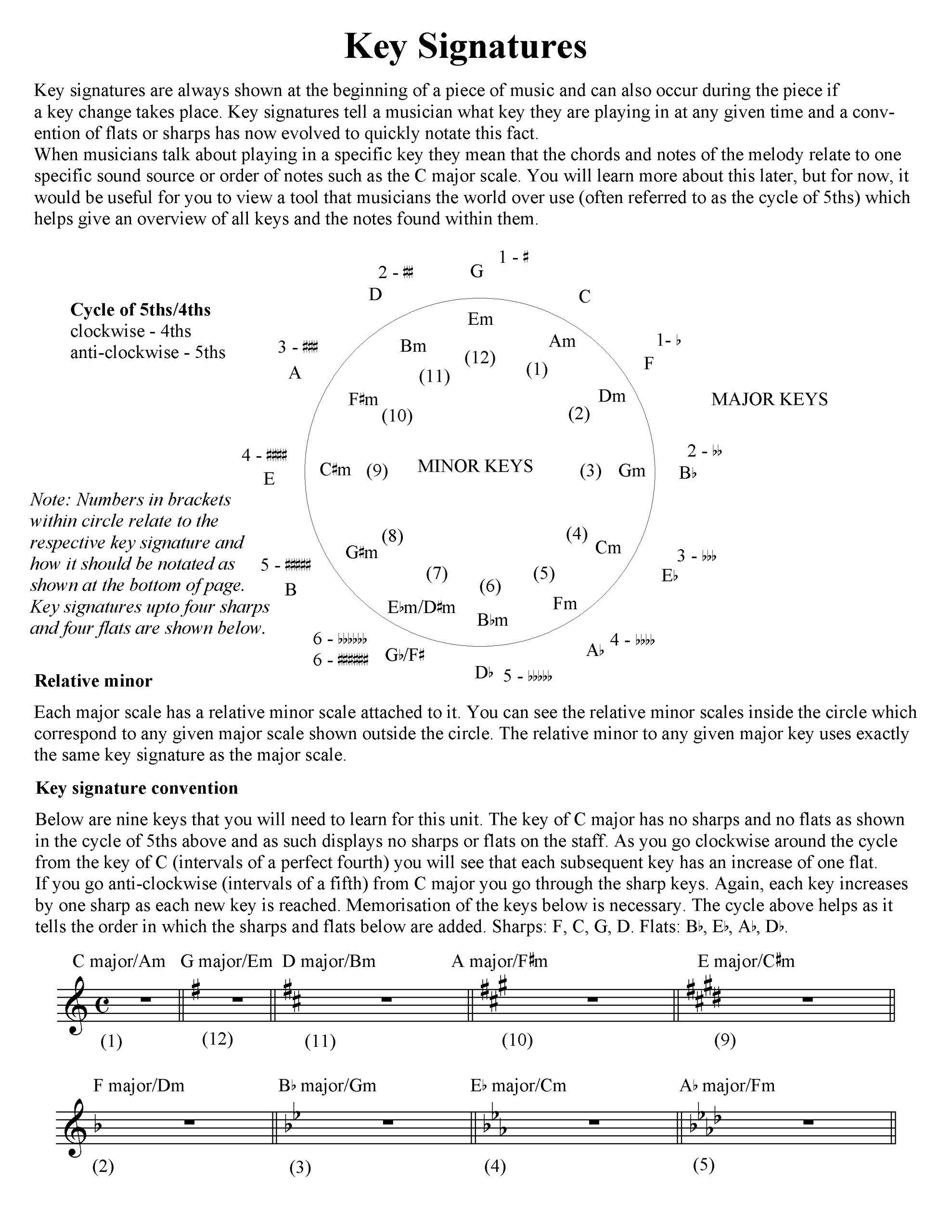
The Role of Clefs in Music Reading
The clef is the compass of music notation. Whether it’s the treble clef spiraling elegantly on higher-pitched sounds or the bass clef anchoring the depths of lower tones, understanding clefs is crucial. They are foundational in reading music across the aural spectrum and, paired with the correct sight reading exercises, these symbols enable you to navigate through octaves and pitches with ease.
Advanced Techniques for Improved Sight Reading
As you continue to improve sight reading skills, embracing more advanced strategies is essential for rapid progress and musical proficiency. At this stage, focus on key areas that enhance your ability to process and perform music at first sight, consolidating your sight reading practice and ensuring you’re utilizing optimal sight reading strategies.
Begin by fine-tuning your preparatory steps. Before playing a note, swiftly identify the key and time signature, which will set the stage for the harmonic and rhythmic framework of the piece. This preliminary insight prepares your mind for the types of accidentals and rhythmic patterns you are likely to encounter.
Next, cultivate the habit of looking ahead. While playing one measure, your eyes should be scanning the next. This technique keeps you constantly prepared for what’s coming up and reduces hiccups in your performance. It’s akin to reading subtitles on a screen; your comprehension and ability to keep up improve substantially when you read a line ahead of the spoken dialogue.
“Sight reading is less about playing what you see and more about anticipating what comes next.”
Develop a deeper understanding of note relationships, which allows you to recognize patterns and make quick adjustments as you play. Moving beyond the reliance on letter names to identify notes can streamline your processing speed.
- Utilize musical tools such as metronomes to maintain a consistent pace, giving you a rhythmic foundation that supports better timing and precision during sight reading.
- Integrate sight reading exercises from specialized books and resources tailored to challenge your current level without overwhelming you.
- Regularly employ sight reading practice sessions in your routine, increasing your exposure to a wide variety of musical styles and compositions.
For a clear illustration of how these techniques can be applied, consider the following table:
| Technique | Benefit | Example Resources |
|---|---|---|
| Identify Key and Time Signatures | Sets harmonic and rhythmic framework | Sight Reading Books with Progressive Difficulty |
| Look Ahead While Playing | Anticipates and prepares for upcoming notes | Practice Pieces with Marked Anticipatory Areas |
| Decipher Note Relationships | Speeds up note recognition and pattern processing | Pattern Recognition Exercises |
| Use of Metronomes | Keeps tempo consistent and supports rhythmic accuracy | Metronomic Apps and Online Tools |
| Dedicated Practice Sessions | Increases fluency in decoding notation | Sight Reading Software and Interactive Apps |
Remember, effective sight reading composes not just the ability to read notes but also to interpret the music expressively. With continued finesse and nuance, your sight reading will not only become accurate but also musically satisfying.
Consistent application of these techniques, coupled with dedicated sight reading practice, will help you master the skill set required for superior sight reading performance. As a musician, your aim is not only to play the notes correctly but to convey the music’s intended emotion and character. Through these advanced techniques, your performances will transform from simply accurate to expressively compelling.
Developing a Practice Routine for Sight Reading
To improve sight reading skills, adopting a structured routine that incorporates sight reading exercises into your daily activities is vital. By introducing consistent, targeted practice, you can streamline your progress and stay motivated. Let’s break down how you can effectively incorporate these practices into your routine for optimal results.
Setting Realistic Goals
Realistic goal setting is the first step towards success in sight reading practice. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced musician, understanding your current level and outlining a step-by-step plan lets you progress at a sustainable pace. Start by choosing pieces within your technical reach and gradually work your way up to more complex compositions. Remember that improving sight reading skills is a marathon, not a sprint. Your patience will be rewarded with steady improvement.
Incorporating Sight Reading into Daily Practice
Consistency yields dividends in the realm of sight reading. Aim to dedicate a portion of your daily practice session specifically to sight reading practice. If your schedule is tight, even just ten minutes a day can result in significant improvements over time. Use a variety of sight reading materials to keep the practice fresh and cover different music styles and difficulties.
Utilizing Metronomes for Better Rhythm
A metronome is an invaluable aid in developing rhythmic precision—crucial for mastering sight reading. Use it during your sight reading practice to help maintain a steady tempo and to challenge yourself with different speeds. As your competence grows, try sight reading exercises with less familiar time signatures to push your rhythmic boundaries.
Follow these guidelines and soon you’ll find that you’re able to approach new pieces with confidence and a greater ease, enjoying the true fruits of your labor.
What You Need to Do to Sight Read Better
Mastering the art of sight reading is not solely about recognizing notes; it’s about crafting a seamless connection between the eyes, the brain, and the fingers. In this journey to enhance your sight reading techniques, certain strategies stand out for their effectiveness in bolstering your abilities quickly. Grasp these practices and integrate them into your music sight reading tips for substantial progress in your sight reading practice.
Enhancing Eye Movements for Quick Recognition
Quick recognition of notes and musical patterns is crucial for efficient sight reading. To train your eye movements, engage in scanning exercises that challenge you to identify key changes, rhythm complexities, and intricate passages in your music pieces before playing them. These exercises will drastically increase your abilities in anticipating musical structures, allowing for a smoother performance.
Memorizing Musical Terms in Italian
Much of the expressiveness in music comes from the interpretation of Italian musical terms. Understanding terms like “allegro” or “fortissimo” provides context to the dynamics and tempo of a piece, which are indispensable cues when sight reading. Commit these terms to memory and you’ll find yourself interpreting pieces with greater nuance and confidence.
Here’s a short list to get you started or perhaps even to find out what you do and don’t know.
Certainly! Here’s a list of common Italian musical terms along with their English equivalents:
- Adagio – Slowly
- Allegro – Fast, lively
- Andante – At a walking pace
- Crescendo – Gradually getting louder
- Decrescendo – Gradually getting softer
- Forte – Loud
- Fortissimo – Very loud
- Piano – Soft
- Pianissimo – Very soft
- Ritardando – Gradually slowing down
- Accelerando – Gradually speeding up
- Legato – Smoothly, connected
- Staccato – Detached, separated
- Pizzicato – Plucked (typically used for string instruments)
- Arco – Played with the bow (opposite of pizzicato)
- Largo – Broadly, slowly
- Vivace – Lively, briskly
- Con moto – With motion
- Con brio – With spirit
- Dolce – Sweetly, softly
- Molto – Very (e.g., molto allegro means very fast)
- Presto – Very fast
- Fermata – Hold or pause
- Coda – Tail, ending section
- Cadenza – Solo passage, often improvised
- Concerto – A musical composition for solo instrument(s) accompanied by an orchestra
- Sonata – A composition for solo instrument or small ensemble
- Trio – A composition or section for three performers
- Quartet – A composition or section for four performers
- Soprano – The highest vocal range
- Alto – The second highest vocal range for women, or the lowest for men
- Tenor – The highest male vocal range
- Bass – The lowest vocal range
- Aria – A solo vocal piece in an opera
- Chorus – A group of singers performing together
- Octave – An interval spanning eight diatonic scale degrees
- Scale – A series of musical notes in ascending or descending order
- Interval – The difference in pitch between two notes
- Key – A group of pitches, or scale upon which a music composition is created
- Tempo – The speed at which a piece of music is played
Mastering the Relationship Between Notation and Sound
The ultimate goal of sight reading is to translate written symbols into sound without hesitation. Developing this skill requires practice in auditory recognition, where you match pitches and rhythms to their notated form. Try vocal sight reading or simple dictation of melodies to strengthen the association between what you see on the page and what you hear in your head.
| Action | Benefit | Practical Tips |
|---|---|---|
| Scan for key changes and rhythmic patterns | Increases anticipation and recognition speed | Isolate complex measures, practice rhythmic clapping |
| Memorize musical expressions in Italian | Deepens interpretative understanding | Use flashcards; associate terms with famous pieces |
| Auditory recognition practice | Strengthens connection between notation and execution | Practice singing pitches, use solfège for melodies |
Sight Reading Techniques for String Instruments
As a string instrument enthusiast looking to improve sight reading skills, it is essential to embrace various sight reading strategies tailored to the unique challenges of string instruments. Before diving into specific techniques, let’s consider how upgrading your sight reading proficiency can transform your musical performance, creating a more seamless and confident connection between your eyes, hands, and the music in front of you.
Improving Fingerboard Knowledge
One of the foundational steps to enhance your sight reading on string instruments is developing comprehensive knowledge of the fingerboard. This requires a strategic approach to practice, starting with familiarization of the notes and positions. Incorporate sight reading exercises into your training regimen that focus on instantly recognizing notes and predicting their locations on the fingerboard, ensuring that your hand movements become second nature.
Fluid Eye Movement and Notation Association
Cultivating fluid eye movement in tandem with accurate notation recognition is paramount. This skill allows you to anticipate what’s coming next in the score without losing your place. Engage in drills that task you with scanning ahead while playing, which will train your eyes to move efficiently across the musical staves. Here’s a simple exercise you can try:
- Set a metronome to a slow tempo.
- As you play a measure, glance at the next one.
- Increase the tempo gradually as you become more comfortable.
String Crossing and Position Shifting
Mastering string crossing and position shifting is also critical for improving your sight reading ability. Begin with exercises that cover the first six positions and pay particular attention to the transitions between them. Utilize sequences involving string crossing to promote agility and accurate intonation across various string combinations.
Let’s summarize some effective practice strategies in the table below:
| Technique | Description | Practice Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Fingerboard Mapping | Understanding the geography of the fingerboard. | Visualize the fingerboard, note names, and finger placements away from your instrument. |
| Note Recognition | Instantly identifying notes on the staff. | Use flashcards with different notes to improve speed and accuracy. |
| Eye Movement | Scanning ahead while playing. | Regularly practice reading one measure ahead of what you are playing. |
| Position Shifting | Moving smoothly between positions. | Practice shifts using scales, focusing on seamless transitions without hesitation. |
In summary, your sight reading skills will significantly improve as you develop and refine your knowledge of the fingerboard, nurture smooth eye movements, and practice string crossings and shifting positions. Remember, the key to mastery lies in consistent and intelligent practice utilizing specific techniques designed for string instruments.
Piano Sight Reading Strategies
For piano aficionados, advancing in sight reading practice means understanding and mastering diverse strategies that address the unique challenges of the instrument. Because both hands often work independently to produce harmonies and melodies, it is vital for pianists to become adept at translating two layers of notation into synchronized musical actions.
Begin by focusing on one hand at a time, which allows you to concentrate on the nuances and technicalities of each staff. Once comfortable, slowly integrate both hands, ensuring that your eye movement is fluid and anticipatory. This gradual increase in complexity will not overwhelm your learning process, but will enhance your ability to sight read with greater confidence and efficiency.
The secret to successful piano sight reading is always to look ahead; establish a tempo that preserves your accuracy, yet stretches your capabilities.
Remember, the ultimate goal of sight reading exercises is to develop a proficiency that allows you to encounter new pieces and perform them with competence at first attempt. To streamline your progress, consider incorporating the following table of exercises into your regular practice regimen:
| Exercise | Description | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Single Hand Practice | Focusing on one hand at a time to play a piece | Improves hand independence and technical control |
| Chord Recognition | Identifying and playing common chord patterns | Enhances harmonic understanding and reduces hesitation |
| Rhythmic Counting | Speaking rhythms out loud before playing | Strengthens rhythmic precision and internal meter |
| Dynamic Reading | Accentuating the dynamics while sight-reading | Develops expressiveness and emotional depth |
| Interval Training | Practicing hand movements between intervals | Assists in swift note-to-note transitions |
Whether you are sitting down to practice for an hour or just have a few minutes, these sight reading exercises can serve as effective warm-ups or full practice pieces. How to get better at sight reading isn’t just about playing music — it’s about immersing yourself in various musical scenarios that challenge your reading and playing abilities.

Turning Musical Theory into Sight Reading Mastery
Embarking on the journey to improve sight reading skills is akin to mastering a new language. Like any language, music has its own grammar, syntax, and vocabulary. By delving into the foundational elements of musical theory, you fortify your ability to interpret and perform at first sight. It’s one thing to understand the theory, but to translate that knowledge adeptly into sight reading prowess requires practice, insight, and a touch of artistry.
Understanding Intervals and Scales
To develop effective sight reading techniques, familiarize yourself with the building blocks of music: intervals and scales. Each interval has a distinct sound, and recognizing these will help you predict melodic direction and harmonies. Scales form the basis for much of Western music. Understanding and memorizing the pattern of whole and half steps in different scales empowers you to navigate the music sheet with confidence.

Translating Rhythms and Melodies from Mind to Instrument
The knack for sight reading also lies in your ability to convert written melodies and rhythms into actual music with fluency. This means internalizing the pulse and noting rhythmic patterns so that you can execute them seamlessly. Anticipate the shape of the melody and let your fingers, breath, or bow respond to the notated pitch changes as if they were second nature.
Learning the Language of Dynamics and Expression
Expressive music sight reading tips encompass more than the notes on the page. You must also become conversant in the language of dynamics and expression—those nuanced Italian terms that breathe life into a piece. Whether it is a gentle pianissimo or a bold fortissimo, the dynamics shape the emotional contour of your performance. Your interpretation of these expressions makes the difference between playing notes and creating a musical experience.
Remember, the ultimate goal of sight reading is not just correctness but musicality. Balancing technical precision with expressive elements requires patience and dedication. As you navigate this path, keep in mind that each piece of music offers a new set of challenges and opportunities—a new language to decode. Embrace it, learn from it, and most importantly, enjoy the process. Your sight reading mastery awaits.
Overcoming Common Challenges in Sight Reading
As you dive into the world of sight reading, you’ll encounter a myriad of challenges that test your musical agility. Don’t be discouraged—this is a normal part of developing your sight reading proficiency. Here are some strategies to help you conquer the most common obstacles you’ll face.
Managing Complexity with Stacked Notes
Stacked notes can be daunting with their vertical clusters demanding quick interpretation. To work through this, sight reading exercises that focus on chord recognition can be immensely helpful. Practice identifying the notes in each chord separately before playing them together to build accuracy and speed.
Staying in Time Without Missing a Beat
A metronome can be your best ally when it comes to keeping time. It is crucial that your sight reading practice sessions include varied rhythmical patterns played with a metronome to cultivate an internal sense of timing. Begin at a slow tempo to ensure precision, then gradually increase the speed as you grow more confident.
Dealing with Asymmetrical and Complex Meters
Complex meters can disrupt even the most experienced musician’s flow. Start by clapping out the rhythm to internalize the beat. Count aloud, emphasize the strong beats, and gradually incorporate the practice into your instrumental play. Remember, understanding and feeling the inherent pulse of asymmetrical and complex meters are key components to successful sight reading strategies.
Tools and Resources to Enhance Your Sight Reading
As you aspire to improve sight reading skills, it’s important to acquaint yourself with the best tools and resources available. Diverse materials such as sight reading exercises and instructional videos are just a click away, ready to transform the way you interpret music. Embrace these aids to elevate your practice session and embark on a journey to sight reading proficiency.

Whether you’re a novice looking for foundational exercises or an advanced musician seeking to finesse your skill, the range of sight reading exercises offered by leading books and software can be monumental in your growth. Let’s explore a table detailing the features of popular tools designed to improve sight reading skills:
| Tool/Resource | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Schirmer’s Library of Musical Classics | A collection of sight reading books that progress in difficulty, ideal for gradual learning. | Individual Practice |
| Musictheory.net | Interactive exercises and lessons on music theory and sight reading. | Self-guided Learning |
| SmartMusic | An educational platform offering a library of music and sight reading exercises with immediate feedback. | Interactive Learning |
| The Sight Reading Project | A web-based resource for sight reading with adjustable difficulty levels and instrumentation. | Ensemble Practice |
| Rhythm Trainer | A digital tool designed to improve rhythmic sight reading with customized settings. | Rhythm Mastery |
| YouTube Tutorials | Free instructional videos offering music sight reading tips and demonstrations. | Visual and Auditory Learners |
These resources not only offer personalized insight into the intricacies of sight reading but also add depth to your learning experience. Incorporating these tools into your practice regime will enable you to tackle various challenges that come with reading music at sight, thereby reinforcing your overall musicianship.
Remember, the key to mastering sight reading is consistent practice. By utilizing these tools and dedicating time to sight reading exercises, you’ll witness a noticeable enhancement in your ability to interpret music swiftly and accurately. So, take advantage of the wealth of resources at your fingertips, and see your sight reading flourish.
Collaborative Sight Reading: Ensemble and Choir Techniques
Engaging in sight reading practice within a group setting enhances not only individual skills but enriches the entire ensemble’s performance. As you join forces to interpret a piece of music for the first time, the shared responsibility of creating a cohesive sound becomes paramount.
Listening to Other Parts and the Whole Ensemble
One key sight reading strategy involves tuning in to the different voices around you. Whether it’s the deep resonances of the cellos, the crisp clarity of sopranos, or the robust brass section, each part contributes to the overall story of the composition. By attentive listening, you learn to synchronize with the ensemble, finding your rightful place within a larger musical tapestry. This practice not only helps to improve sight reading skills but fosters a sense of unity and anticipation for what’s to come. Remember, while sight reading, you’re not just playing notes, you’re telling a collective story.
Visualizing the Score While Playing
When immersed in ensemble sight reading, envisaging the score becomes vital. It’s about understanding the context where your line fits within the broader scope of the music. Like an intricate dance, your eyes may focus on your specific steps, yet you’re always aware of the surrounding movement. This visualization technique aids in preparing for the unexpected turns and keeps you aligned with the group’s rhythm and dynamics.
Adapting to Different Musical Styles and Characters
Each piece of music comes with its unique character and style which, when sight reading, you’re often meeting for the first time. Adaptability is key. One moment you could be flowing through a Baroque fugue, and the next, syncopating a modern jazz standard. This constant change of musical personas is what makes sight reading so exhilarating. Embrace each style; let it inform your technique, expression, and dynamics. Over time, your versatility will expand, and your ability to swiftly adjust will become second nature.
Let’s explore some core components through a detailed table that will not only help you in ensemble settings but also bolster your overall musicianship:
| Technique | Benefit | Application in Ensemble |
|---|---|---|
| Listening to other parts | Improves rhythmic and harmonic awareness | Allows for better blending and balance within the group |
| Score visualization | Enhances memory and anticipation of musical phrases | Contributes to a more unified interpretation of the music |
| Adapting to styles | Expands musical vocabulary and responsiveness | Equips the ensemble to tackle a diverse repertoire with confidence |
Incorporating these sight reading strategies into your practice can significantly improve sight reading skills, giving you the confidence to perform with precision and expressiveness, regardless of the setting or musical genre. And always remember, whether in a solo or group setting, sight reading is about bringing the joy and spontaneity of music to life on the very first try.
Embracing Technology: Apps and Online Tools for Sight Reading
Technology has transformed the landscape of musical education, offering you a plethora of apps and tools that aim to excel your sight reading skills. These innovative solutions cater to a variety of learning styles and can significantly supplement your sight reading practice. Not only can they make learning more interactive and engaging, but they also bring expert guidance to the palm of your hand.
Interactive Sight Reading Software
Interactive software makes sight reading exercises fun and effective by providing real-time feedback on your performance. These tools often have a library of musical scores to practice with, ranging from simple melodies to complex compositions, allowing you to gradually increase the level of difficulty as your confidence grows. It’s like having a virtual teacher who’s available 24/7 to guide you on how to get better at sight reading.
Virtual Metronomes and Rhythm Trainers
Rhythm is a cornerstone of music and sight reading, and virtual metronomes and rhythm trainers are indispensable tools for developing precision. These devices enable you to maintain a consistent tempo, which is crucial when reading a new piece for the first time. They introduce various rhythmic patterns to challenge you and improve your timing, ultimately enhancing your overall sight reading practice.
The Role of Online Videos in Music Education
Online education has seen a dramatic surge, and this includes lessons in music and sight reading. Platforms such as YouTube are home to thousands of tutorials that range from beginner to advanced levels. Experienced musicians share insights and tips on sight reading, offering multiple perspectives and techniques to enrich your practice. These resources are invaluable for expanding your understanding and ability in sight reading.
Conclusion
Embarking on the path to improve sight reading skills is much like setting forth on a musical expedition where every note, every rhythm becomes a stepping stone towards greater proficiency. As you reflect on the journey of sight reading improvement, it’s essential to recognize the progress you’ve made, as well as the areas that offer opportunities for further growth. Whether you’re a budding musician or a seasoned performer, the dedication to this craft is a testament to your passion for music and your desire to access its fullest potential.
Reflecting on the Journey of Sight Reading Improvement
Throughout this exploratory process, you’ve encountered various sight reading exercises, each designed to unpack the vast language of music. Your commitment to deciphering new scores, recognizing patterns, and understanding musical structure has deepened your relationship with your instrument and the music you create. Remember that this journey is as unique as your musical voice, shaped by your individual challenges and triumphs.
Consistency and Patience in Developing Skills
Developing extraordinary sight reading abilities doesn’t happen overnight. It requires consistency and patience, often asking you to revisit basics and refine skills through deliberate practice. When you find yourself daunted by a complex piece or stumbling over unfamiliar phrases, it’s your resilience that will guide you back to the melody line. It’s about what you need to do to sight read better daily, fostering your innate talent with unwavering perseverance and a metronomic heartbeat of dedication.
Continued Learning for Lifelong Musical Enjoyment
The beauty of the sight reading process is that it never truly ends — there’s always a new piece, genre, or technique to conquer, which means your musical journey is perpetually unfolding. As you continue to immerse yourself in scores and rhythms, savor the satisfaction that comes from bringing silent notes to life. After all, your willingness to lean into lifelong learning is what keeps the music playing, the pages turning, and your passion for sight reading ever-evolving.
FAQ
What are the basic skills I need for sight reading music?
The basic skills for sight reading include understanding music notation, recognizing key and time signatures, and knowing the roles of different clefs. Get comfortable with these fundamentals, as they are your building blocks for sight reading.
How can I improve my sight reading skills?
Improvement comes with practice. Start by incorporating sight reading into your daily routine, using a metronome to keep steady time, and setting realistic goals for your progress. Over time, practice with varied material to encounter and master a wider range of musical challenges.
What advanced techniques can I use to sight read better?
Advanced techniques include looking ahead in the music while playing, identifying key and time signatures before beginning, and understanding the relationship between written notation and the resulting sound. Focus on improving your ability to decode complex note relationships on sight.
How should I practice sight reading on string instruments?
For string instruments, good sight reading involves a comprehensive understanding of the fingerboard, the ability to coordinate your eye movements quickly with note recognition, and mastery in string crossings and position shifts. Employ specific exercises designed to enhance these particular skills.
What strategies are there for piano sight reading?
Pianists should practice managing both hands’ layers of notation, coordinating their actions while keeping their eyes moving ahead in the score. Start with one hand’s part and gradually combine both, maintaining a comfortable pace for complexity.
Why is memorizing musical terms important in sight reading?
Memorizing musical terms, especially those in Italian, is crucial because they inform the expressive qualities of the piece. Knowing these terms helps in understanding and executing the dynamics, articulations, and tempo modifications indicated in the score accurately.
How can I enhance my eye movement for sight reading?
Practice scanning the music before you begin playing. Look for patterns, spot difficult passages, and train your eyes to move ahead of where you are currently playing. This will help you anticipate what’s coming and reduce the likelihood of being caught off guard by sudden changes.
Are there any tools that can help me improve my sight reading?
Yes, there are many resources to help you improve. Use dedicated sight-reading books that increase in difficulty, metronomes for rhythm, software apps designed for sight reading practice, and watch online tutorial videos from experienced musicians. All these tools can be beneficial for your practice.
What are some common sight reading challenges and how do I overcome them?
Common challenges include playing stacked notes, maintaining tempo without missing beats, and navigating complex meters. Overcome these by practicing pieces with these specific elements, using a metronome to keep steady time, and breaking difficult passages down into smaller, manageable parts.
What sight reading techniques are useful for ensemble and choir settings?
Techniques for ensemble and choir settings include listening closely to other parts, visualizing the score while focusing on your own part, and being flexible with different musical styles and characters. This collaborative approach helps to create a cohesive sound and enhances overall performance quality.
How are technology and online tools changing the way we learn sight reading?
Technology offers personalized learning experiences through interactive apps, virtual metronomes, and rhythm trainers to assist with timing, and online videos for visual and auditory learning aids. These tools provide innovative ways to develop sight reading skills and support both self-taught progress and guided lessons.
How long does it take to get better at sight reading?
Improving sight reading is a gradual process that varies by individual. Consistency, patience, and regular practice are vital for seeing improvement. As you continue to learn and challenge yourself with new material, your sight reading will naturally get better over time.
Source Links
- https://www.thestrad.com/playing-hub/10-tips-to-improve-your-sight-reading/16.article
- https://www.hoffmanacademy.com/blog/acquiring-fluency-music-becoming-great-sight-reader/
- https://zuerichgitarrenunterricht.ch/en/6-ways-to-improve-your-sight-reading-on-the-piano/
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon associate, Google associate as well as associate for other programs, Guitar & Music Institute may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.