This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon associate, Google associate as well as associate for other programs, Guitar & Music Institute may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.

Welcome to our guide on jazz guitar chords! Whether you’re a beginner looking to learn jazz guitar chords or an advanced player seeking to expand your repertoire, mastering these essential jazz guitar chords is crucial for playing jazz music with style and authenticity.
Jazz guitar chords add a certain sophistication and richness to your playing, opening up a world of expressive possibilities. They are the building blocks of jazz harmony, allowing you to create lush, colorful, and melodic sounds.
In this article, we will introduce you to 10 must-know jazz guitar chords that will enhance your playing and enable you to explore the beauty of jazz music. From major seventh chords to dominant ninths and diminished sevenths, we will cover a range of chord types and voicings that are essential for any jazz guitarist.
Key Takeaways:
- Learning jazz guitar chords is important for playing jazz music with authenticity.
- Jazz chords add richness, depth, and expressiveness to your playing.
- Mastering essential jazz guitar chords is crucial for building a strong foundation.
- Understanding chord voicings and voice leading contributes to the overall sound of jazz progressions.
- Exploring different chord types and voicings allows for versatility and creativity in jazz guitar playing.
The Beauty of Jazz Guitar Chords
In this section, we will explore the unique qualities and beauty of jazz guitar chords. Jazz chords have a captivating expressiveness that adds richness and depth to your playing. They have the power to evoke a wide range of emotions and create a dynamic and captivating musical experience.
Jazz guitar chords are known for their colorful and versatile nature. They incorporate complex harmonies, incorporating extended notes and altered tones, allowing you to add unique flavors to your compositions. The interplay of different chord voicings and inversions creates a vibrant and harmonically rich sound.
Whether you are playing soulful ballads or upbeat swing tunes, jazz guitar chords unlock endless creative possibilities. They provide a melodic and harmonic foundation that allows you to improvise and express yourself with freedom and inventiveness. The subtle nuances and nuances of jazz guitar chords enable you to paint a vivid musical landscape and engage your listeners in a captivating journey.
Next, let’s dive into the fascinating world of jazz guitar chord voicings and explore the different structures and techniques that make them so compelling.
Understanding Jazz Guitar Chord Voicings
The Structure of Voicings
Jazz guitar chord voicings play a crucial role in creating the distinct sound of jazz music. These voicings, also known as chord shapes, determine the arrangement and placement of the notes within a chord. By understanding the structure of voicings, you can effectively voice chords and create harmonic variations that add depth and complexity to your playing.
Voicings are constructed by selecting specific notes from a chord and arranging them in a particular order. They can consist of three, four, or more notes, depending on the complexity of the desired sound. The arrangement of these notes can greatly impact the overall feeling and character of the chord.
When constructing voicings, it’s essential to consider the chord structure. Different types of chords, such as major, minor, dominant seventh, and extended chords, have their own unique combinations of intervals that create their distinct sound. By understanding the intervallic makeup of each chord type, you can create voicings that accurately represent their characteristic sound.
“Understanding the structure of voicings is the key to unlocking the full potential of jazz guitar chord voicings. It allows you to create rich and expressive harmonies that bring your playing to life.”
Importance of Voice Leading in Jazz
Voice leading is an essential concept in jazz guitar chord voicings. It refers to the smooth and logical movement of individual voices or notes within a chord progression. By applying good voice leading techniques, you can create seamless transitions between chords, resulting in a harmonically cohesive and pleasing musical experience.
In jazz, voice leading is crucial because it helps maintain the melodic flow and harmonic clarity of the music. It ensures that each note within a chord progression smoothly connects to the next, creating a strong sense of musical continuity. Voice leading also allows you to highlight melodic lines and create interesting harmonic tension and resolution.
To achieve effective voice leading, it’s important to consider the voice leading principles, such as minimizing melodic leaps, resolving dissonances, and utilizing common tones between chords. By consciously applying these principles, you can craft chord progressions that are not only musically satisfying but also showcase your proficiency as a jazz guitarist.
Voicing Types: Drop 2, Drop 3, and More
There are various types of jazz guitar chord voicings that you can explore and incorporate into your playing. Two popular voicing techniques are drop 2 and drop 3 voicings.
Drop 2 voicings involve taking a four-note chord and dropping the second-highest note down an octave. This results in a voicing that has a wide span on the fretboard and allows for easy voice leading. Drop 2 voicings are commonly used in comping and soloing situations.
Drop 3 voicings, on the other hand, involve taking a four-note chord and dropping the third-highest note down an octave. These voicings have a more spread-out sound and are often used in chord melody arrangements and comping.
In addition to drop 2 and drop 3 voicings, there are many other voicing techniques and variations to explore, such as rootless voicings, three-note voicings, and quartal voicings. Each technique offers its own unique sound and possibilities for jazz guitar chord voicings.
By familiarizing yourself with these different voicing types and experimenting with their application, you can expand your chord vocabulary and add versatility to your playing.
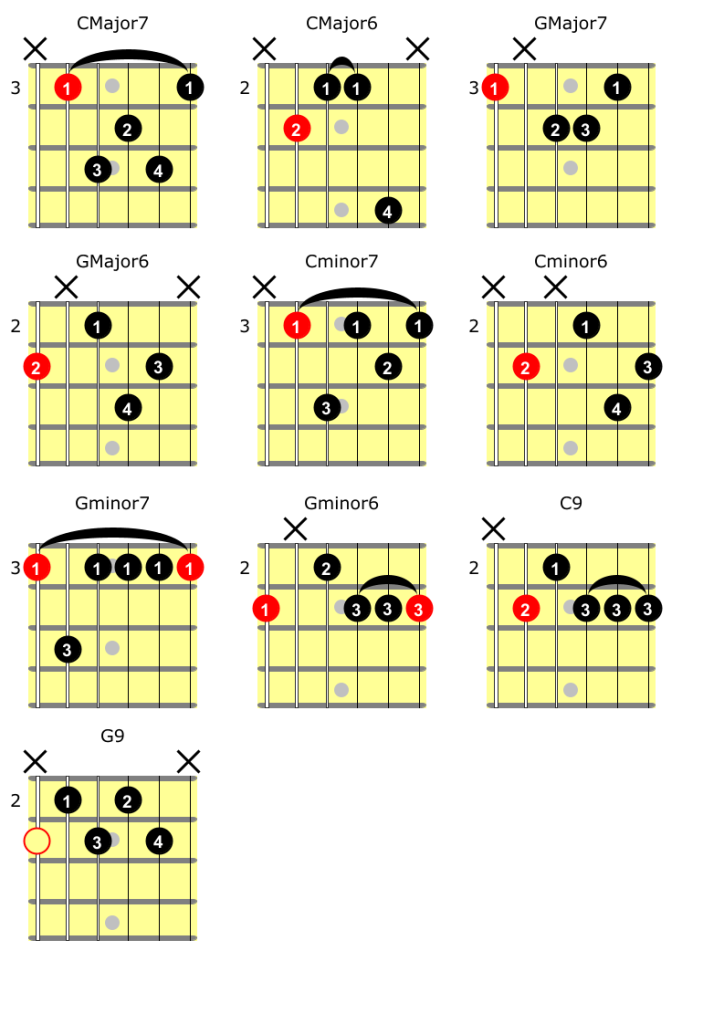
Major Seventh: The Quintessential Jazz Chord
In jazz music, the major seventh chord holds a special place. Its lush and sophisticated sound has made it one of the quintessential chords in the genre. Understanding the construction and characteristics of major seventh chords is essential for any jazz guitarist.
The major seventh chord consists of four notes: the root, major third, perfect fifth, and major seventh. These notes combine to create a chord that exudes a sense of warmth and richness. Its unique qualities make it a versatile choice for jazz musicians looking to add color and depth to their playing.
Exploring different shapes and voicings of major seventh chords allows guitarists to express their musical ideas in various ways. There are several common major 7th chord shapes, such as the open position, barre chords, and movable shapes. Each shape provides a different voicing and allows for different melodic possibilities.
Major seventh chords are used extensively in jazz chord progressions. Their smooth and melodic nature makes them particularly suitable for creating lush and harmonically rich sequences. In jazz standards like “Misty” and “Somewhere Over the Rainbow,” major seventh chords can be found embellishing the melodies and adding a touch of elegance to the harmonic landscape.
Using major seventh chords in jazz requires an understanding of their function within the context of a song. They often serve as tonic chords, establishing a sense of resolution and stability. They can be used as standalone chords or as part of more complex progressions, providing a rich harmonic foundation for improvisation and melodic exploration.
Minor Seventh: The Sound of Sophistication
The minor seventh chord is an essential component of jazz music, known for its sophisticated and melancholic sound. It adds a touch of elegance and emotion to your playing, allowing you to create more nuanced and expressive musical phrases.
When comparing the minor seventh chord to other minor chords, such as the regular minor triad, you’ll notice that the addition of the seventh (usually a minor seventh interval) adds a subtle tension and complexity to the chord. This tension creates an intriguing contrast that captures the listener’s attention and contributes to the overall mood of the music.
To use minor seventh chords effectively in jazz, it’s important to familiarize yourself with their different shapes and voicings. Experiment with various fingerings and positions on the guitar neck to discover the voicings that resonate with your playing style and musical preferences. This exploration will not only broaden your repertoire of minor seventh chord progressions but also enhance your overall understanding of chord voicing techniques.
To help you practice and master minor seventh chords, here are a few tips:
- Start by learning the basic minor seventh chord shapes in open and barre positions. These shapes serve as a foundation for building more complex voicings.
- Practice playing minor seventh chord progressions in different keys. This will improve your ability to navigate the fretboard and effortlessly switch between chords during improvisations.
- Explore different rhythmic patterns and strumming techniques to add dynamics and interest to your chord playing.
- Experiment with chord substitutions and variations to create unique and personalized chord progressions.
By regularly incorporating minor seventh chords into your practice routine, you’ll develop a deeper understanding of their harmonic potential and gain the confidence to use them in a variety of musical contexts. Whether you’re playing jazz standards, composing your own compositions, or simply jamming with fellow musicians, the versatility and sophistication of minor seventh chords will elevate your playing to new heights.

| Chord Shape | Fingering | Diagram |
|---|---|---|
| Open Position | X32010 | |
| Barre Position | 5x555x | https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=HUABCBA7KZ8 |
| Root on 5th String | x7978x |
Dominant Ninth: Extending Beyond the Basics
In jazz music, the dominant ninth chord adds an extra layer of complexity and sophistication to your playing. This chord, comprised of the root, major third, perfect fifth, minor seventh, and major ninth, has a rich and distinctive sound that is commonly used in jazz chord progressions.
To fully utilize the dominant ninth chord in your jazz guitar playing, it’s important to familiarize yourself with different shapes and voicings. By mastering a variety of dominant ninth chord shapes, you can effortlessly navigate the fretboard and create interesting melodic lines.
One of the most common shapes for the dominant ninth chord is the “C9” shape, which is based on the A string root position. It involves placing your index finger on the 8th fret of the A string, your middle finger on the 9th fret of the D string, your ring finger on the 10th fret of the G string, and your pinky finger on the 10th fret of the B string. Strumming all the strings will produce a full and rich dominant ninth chord sound.
Another popular voicing is the “E9” shape, which is based on the E string root position. This shape involves placing your index finger on the 7th fret of the A string, your middle finger on the 9th fret of the D string, your ring finger on the 7th fret of the G string, and your pinky finger on the 8th fret of the B string. Strumming all the strings will give you a bright and vibrant dominant ninth chord.
The dominant ninth chord can be used in various progressions to add tension, create movement, and resolve to other chords. For example, in a ii-V-I progression in the key of C major, you can substitute the V7 chord with a dominant ninth chord (G9) to enhance the harmonic color and create a smooth resolution.
Here’s an example of a jazz chord progression that incorporates the dominant ninth chord:
[Chord Progression Example]
- Am7 – D7
- G9 – Cmaj7
By using dominant ninth chords in jazz, you can elevate your playing and explore new harmonic possibilities. Experiment with different shapes, progressions, and voicings to develop your own unique style and sound.
Diminished Seventh: Tension and Release
In jazz music, the diminished seventh chord is known for its unique qualities that create tension and release. This chord consists of consecutive minor thirds, giving it a dissonant and unstable sound. However, when used correctly, it can add a lot of excitement and color to your chord progressions.
To effectively use diminished sevenths in progressions, it’s important to understand their role in creating tension and resolving it. Diminished seventh chords naturally want to resolve to a more stable chord, often a major or dominant seventh chord. By incorporating these chord progressions into your playing, you can create a sense of forward motion and musical tension that captivates listeners.
When navigating diminished seventh chord shapes, it’s helpful to explore different voicings and inversions to find the most comfortable and musically pleasing shapes on the guitar neck. Practicing various voicings and fingerings will enable you to seamlessly transition between chords and create smooth melodic lines.
Diminished Seventh Chord Exercises
To further develop your skills with diminished seventh chords, try incorporating the following exercises into your practice routine:
- Play diminished seventh arpeggios in different positions on the guitar neck.
- Experiment with different rhythmic patterns and strumming techniques when playing diminished chords.
- Create chord progressions that utilize diminished seventh chords in interesting and unexpected ways.
- Transpose familiar songs or chord progressions into different keys using diminished seventh chords.
By regularly practicing these exercises, you’ll become more comfortable with diminished seventh chords and be able to confidently incorporate them into your jazz guitar playing.
Table
| Diminished Seventh Chord | Diminished Seventh Chord Shapes |
|---|---|
| Diminished Seventh Chord | Shape 1 |
| Shape 2 | |
| Shape 3 |
Minor Sixth: Crafting Moods with Chords
In the world of jazz music, chords play a significant role in creating the desired atmosphere and mood. One such chord that adds a touch of melodic and moody qualities is the minor sixth chord. With its distinct sound, the minor sixth chord can evoke a range of emotions in your playing.
The construction of the minor sixth chord involves combining a minor triad with a major sixth interval. This unique combination results in a chord that is harmonically rich and full of character. The minor sixth chord can be played in various shapes and voicings across the guitar neck, allowing for creativity and exploration in your playing.
When utilized in jazz music, the minor sixth chord can help craft different moods and express a wide range of emotions. Its melancholic and introspective qualities make it ideal for ballads and introspective compositions. Whether you’re looking to create a pensive and reflective atmosphere or add a touch of nostalgia to your jazz improvisation, the minor sixth chord is a versatile tool in your musical arsenal.
To illustrate the versatility and diverse applications of the minor sixth chord in jazz, let’s take a look at a table showcasing different shapes and voicings:
Minor Sixth Chord Shapes and Voicings
| Shape | Voicing |
|---|---|
| Shape 1 | Voicing 1 |
| Shape 2 | Voicing 2 |
| Shape 3 | Voicing 3 |
As shown in the table, the minor sixth chord can be expressed in different shapes and voicings, allowing for variations in tone and texture. Exploring these different shapes and voicings will not only expand your chord vocabulary but also enhance your ability to convey different moods and emotions in your jazz playing.
Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced jazz guitarist, incorporating minor sixth chords into your playing can elevate your musical expression and captivate your audience. Experiment with different shapes, voicings, and progressions to discover the endless possibilities that the minor sixth chord holds in the world of jazz.
The Versatile Dominant Seventh Chord
In both blues and jazz music, the dominant seventh chord plays a vital role in creating rich and expressive harmonies. Its versatility allows it to add tension, color, and a sense of resolution to chord progressions. Understanding the dominant seventh chord and its various applications is essential for any guitarist looking to delve into the world of blues and jazz.
Dominant Seventh in Blues and Jazz
In blues music, the dominant seventh chord is a cornerstone of the genre. It creates the characteristic blues sound and provides a foundation for improvisation. The dominant seventh chord shapes the sound of the blues progression and is often used in combination with other chords to create tension and release. Its powerful and soulful qualities make it a favorite among blues guitarists.
In jazz music, the dominant seventh chord is a staple in countless compositions and improvisations. It serves as a primary chord choice for dominant chord progressions and functions as a stepping stone to resolve tensions. Whether it’s a ii-V-I turnaround or a bluesy jazz tune, the dominant seventh chord adds complexity and sophistication to the harmonic landscape.
Altering the Dominant Seventh for Flavor
To spice up your blues and jazz playing, you can experiment with alterations of the dominant seventh chord. Common alterations include adding a sharp or flat ninth, sharp or flat fifth, or sharp eleventh. These alterations can bring unique flavors and colors to your chord progressions and improvisations.
Experiment with altered dominant seventh chords to add tension, intrigue, and a touch of unpredictability to your playing.
Playing around with different variations of the dominant seventh chord can lead to fresh and unexpected sounds, allowing you to create your own unique style. Alterations can also enhance your ability to navigate complex chord progressions and provide new opportunities for improvisation and creativity.
Dominant Seventh Chord Substitutions
In addition to altering the dominant seventh chord, you can also explore substitutions. Dominant seventh chord substitutions involve replacing a dominant seventh chord with another chord that shares similar harmonic properties. These substitutions can introduce new harmonic flavors and expand your musical palette.
Some common dominant seventh chord substitutions include the tritone substitution, where you replace a dominant seventh chord with another chord whose root is a tritone away, and the diminished chord substitution, where you use a diminished seventh chord as a substitute for the dominant seventh chord.
By incorporating dominant seventh chord substitutions into your playing, you can create unexpected and exciting harmonic progressions, adding depth and complexity to your compositions and improvisations.
Jazz Guitar Chords for Beginners
If you’re just starting out on your jazz guitar journey, it’s crucial to begin with the right foundation. In this section, we will provide you with a selection of beginner-friendly jazz guitar chords that will set you on the right path. These chords are designed to be easy to play while still capturing the essence of jazz music.
By focusing on these essential jazz guitar chord shapes and voicings, you will develop a solid understanding of the harmonic language of jazz. Practice is key, so we will also provide you with exercises to help you strengthen your finger dexterity, chord transitions, and overall playing technique.
With these easy jazz guitar chords, you can start exploring the world of jazz music and begin to develop your unique jazz guitar sound. Let’s dive in!
Check out the GMI Guitar Shop which has a large amount of free jazz guitar resources for you to download right now.
Advanced Jazz Guitar Chord Substitutions
In jazz music, chord substitutions are a powerful tool that can take your playing to the next level. By substituting chords in standard progressions, you can add complexity, interest, and harmonic depth to your compositions. In this section, we will explore advanced jazz guitar chord substitutions and uncover the methods behind them.
Substituting Chords in Standard Progressions
When substituting chords in standard progressions, the goal is to create tension and release, while maintaining the overall harmonic structure. This allows for a fresh and unique interpretation of familiar chord progressions. By substituting specific chords, you can add unexpected twists and turns to your music, captivating your audience and showcasing your artistic prowess.
One popular and powerful technique in jazz guitar chord substitutions is the tritone substitution. Let’s dive into the theory and application of this compelling substitution.
The Tritone Substitution: What and How
The tritone substitution is a technique where you replace a dominant seventh chord with another dominant seventh chord that is a tritone (three whole steps or six half steps) away. For example, if you have a G7 chord, you can substitute it with a Db7 chord, as the interval between G and Db is a tritone.
This substitution works because the tritone interval contains two important chord tones: the 3rd and 7th. These two tones define the quality of the chord and give it its dominant character. By transposing the tritone, you are essentially swapping the 3rd and 7th, resulting in a different chord with a similar function. This substitution creates an intriguing tension that resolves melodically, adding an element of surprise and intrigue to your progressions.
To better understand and implement tritone substitutions in your playing, let’s look at some examples and exercises:
- Choose a familiar jazz standard progression and identify the dominant seventh chords within it.
- Replace each dominant seventh chord with its tritone substitution.
- Play through the new progression and experiment with different voicings and rhythms.
- Listen to recordings of jazz musicians applying tritone substitutions to gain inspiration.
- Gradually incorporate tritone substitutions into your improvisations and compositions.
By practicing tritone substitutions, you will develop a deeper understanding of chord functions, expand your harmonic palette, and enhance your overall musicality. Embrace the complexity and versatility of advanced jazz guitar chord substitutions, and let your creativity soar.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering jazz guitar chords is essential for elevating your playing to new heights. These chords add depth, richness, and expressiveness to your music, allowing you to capture the true essence of jazz. However, it’s important to remember that mastering jazz guitar chords requires practice, persistence, and creative exploration.
By incorporating jazz guitar chords into your musical repertoire, you open up a world of possibilities for your playing. Whether you’re a beginner or an advanced guitarist, these chords can enhance your improvisation, composition, and overall musicality. So don’t be afraid to experiment and push the boundaries of what you can do with jazz guitar chords.
Remember, the journey to mastering jazz guitar chords may not always be easy, but with dedication and consistent practice, you will see significant improvement over time. So keep practicing, keep exploring, and most importantly, keep playing. Incorporate jazz guitar chords into your playing and watch as your music comes alive with the vibrant spirit of jazz.

FAQ
What are the 10 essential jazz guitar chords that every guitarist should know?
The 10 essential jazz guitar chords are major seventh, minor seventh, dominant ninth, diminished seventh, minor sixth, dominant seventh, major sixth, half-diminished seventh, augmented major seventh, and augmented seventh.
How do jazz guitar chords add richness, depth, and expressiveness to your playing?
Jazz guitar chords add richness, depth, and expressiveness to your playing by incorporating extended and altered tones that create complex harmonic textures and colorful voicings.
How are jazz guitar chord voicings built?
Jazz guitar chord voicings are built by selecting specific notes from a chord and arranging them in a way that best fits the desired sound, range, and voice leading of the chord progression.
What is the importance of voice leading in jazz?
Voice leading in jazz is crucial for achieving smooth and connected chord progressions. It involves moving the individual voices of a chord in a logical and musically pleasing manner.
What are the different types of jazz guitar voicings?
The different types of jazz guitar voicings include drop 2, drop 3, rootless, and close position voicings. Each type has its own unique sound and application in jazz music.
What is the major seventh chord and how is it used in jazz?
The major seventh chord is a four-note chord consisting of the root, major third, perfect fifth, and major seventh. It is commonly used in jazz for its bright and lush sound, often found in ballads, bossa nova, and other jazz standards.
What are the characteristics of the minor seventh chord?
The minor seventh chord is a four-note chord consisting of the root, minor third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. It has a melancholic and sophisticated sound and is commonly used in jazz for its mellow and expressive qualities.
How is the dominant ninth chord used in jazz?
The dominant ninth chord is a five-note chord consisting of the root, major third, perfect fifth, minor seventh, and major ninth. It is commonly used in jazz to add tension and color to dominant chords, creating a more complex and interesting harmonic sound.
What is the diminished seventh chord and how is it applied in jazz?
The diminished seventh chord is a four-note chord consisting of the root, minor third, diminished fifth, and diminished seventh. It is used in jazz to create tension and enhance harmonic movement, often resolving to a major or dominant chord.
How can the minor sixth chord be used to craft different moods in jazz?
The minor sixth chord is a four-note chord consisting of the root, minor third, perfect fifth, and major sixth. It can be used in jazz to create a variety of moods, such as dreamy, melancholic, or even exotic sounds.
What is the role of the dominant seventh chord in blues and jazz music?
The dominant seventh chord plays a crucial role in both blues and jazz music. In blues, it is used as the primary chord, while in jazz, it is used to create tension and provide a strong resolution to the tonic chord.
What are some beginner jazz guitar chords that are essential to learn?
Some essential beginner jazz guitar chords include major seventh, minor seventh, dominant seventh, major sixth, and minor sixth chords. These chords provide a strong foundation for playing jazz music.
What are some advanced jazz guitar chord substitutions?
Advanced jazz guitar chord substitutions include techniques such as tritone substitution, chord inversions, and reharmonization. These techniques add complexity and interest to standard chord progressions.
Why is it important to master jazz guitar chords?
Mastering jazz guitar chords is essential for becoming a well-rounded jazz guitarist. They provide the foundation for improvisation, harmonization, and creating unique chord progressions that define the jazz sound.
Source Links
- https://truefire.com/guitar-chords-lessons/10-jazz-guitar-chords-you-must-know/c2658
- https://www.jazzguitar.be/blog/jazz-chord-progressions/
- https://www.roadiemusic.com/blog/10-essential-jazz-guitar-chords/
This post may contain affiliate links. As an Amazon associate, Google associate as well as associate for other programs, Guitar & Music Institute may earn commissions from qualifying purchases.